Cold Chain
Product Type: All
Stage: Handing & Storage, Distribution & Marketing
Problem: Quality of products during transport in the hot summer season causes wastage and carbon emissions.
Solution: From the Kinnow project in India, Carrier calculated that food loss was reduced by 76% and carbon emissions by 16%. While Carrier was in charge of conducting the study and creating communication tools to engage farmers and government authorities, farmers themselves have to invest in the technology in order to realize the benefits from the cold chain.
1. Check storage time with refrigeration: In other words analyze for how long you can store your product before it is consumed.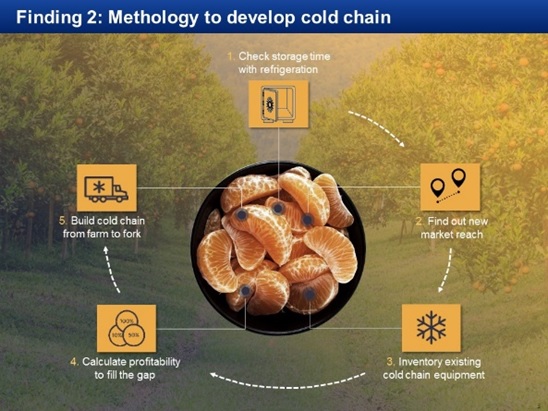
2. Find out new market reach: This involves the location and time in which your product reaches the market and the price/value it will receive depending on these factors.
3. Inventory existing cold chain equipment: In some cases farmers may not even notice that cooling technology can provide benefits and during this phase some knowledge sharing may be involved.
4. Calculate profitability to fill the gap: It is possible that certain fruits do not yield profit from the investment in a cold chain because their market value is too low, therefore, a transparent analysis of the profitability is important before establishing a cold chain.
5. Build cold chain from farm to fork: Infrastructure, logistics and additional services.
6. Four pillars that Carrier uses to respond to the need of reducing FLW and improving cold chains for different valuable crops. The pillars are Technology, Education, Partnership, and Research.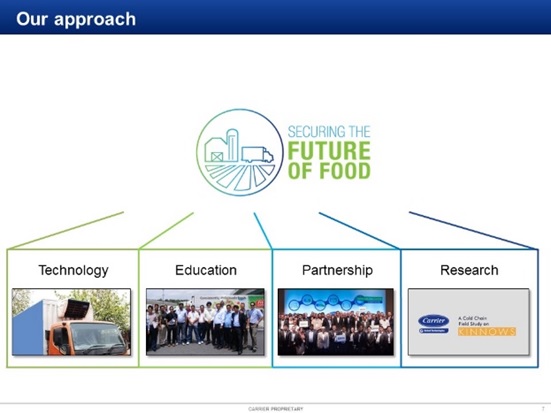
Carrier Refrigeration Co.(Mr. Eric Prieur, Cold Chain Sustainability Director)
